LAYER 3 SWITCH - A Layer 3 switch can act as a Layer 2 switch (that is, making forwarding decisions based on MAC addresses), or it can make forwarding decisions based on Layer 3 information (for example, IP address information).
SWITCHED VIRTUAL INTERFACE (SVI) - You can configure the IP address for a collection of ports belonging to a VLAN under a virtual VLAN interface. This virtual VLAN interface is called a switched virtual interface - SVI.
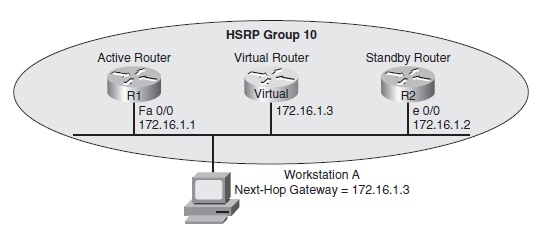
HOT STANDBY ROUTING PROTOCOL (HSRP) - HSRP uses virtual IP and MAC addresses. One router, known as the active router, services requests destined for the virtual IP and MAC addresses. Another router, known as the standby router, can service such requests in the event the active router becomes unavailable. HSRP is Cisco proprietary.
VIRTUAL ROUTER REDUNDANCY PROTOCOL (VRRP) - VRRP, similar to Hot Standby Routing Protocol (HSRP), allows a collection of routers to service traffic destined for a single IP address. Unlike HSRP, the IP address serviced by a VRRP group does not have to be a virtual IP address. The IP address can be the address of a physical interface on the virtual router master, which is the router responsible for forwarding traffic destined for the IP address of the VRRP group.
GATEWAY LOAD BALANCING PROTOCOL (GLBP) - GLBP can load-balance traffic destined for a next-hop gateway across a collection of routers, known as a GLBP group. Specifically, when a client sends an Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) request, in an attempt to determine the MAC address corresponding to a known IP address, GLBP can respond with the MAC address of one member of the GLBP group. The next request would receive a response containing the MAC address of a different member of the GLBP group. GLBP is Cisco proprietary.
CONTROL PLANE - The control plane of operation encompasses protocols used between routers and switches. These protocols include, for example, routing protocols and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP). Also, a router or switch's processor and memory reside in the control plane.
BACKPLANE - The backplane of a switch physically interconnects a switch's ports. Therefore, depending on the specific switch architecture, frames flowing through a switch enter via a port (that is, an ingress port), flow across the switch's backplane, and are forwarded out of another port (that is, an egress port).
TERNARY CONTENT ADDRESSABLE MEMORY (TCAM) - TCAM is a special type of memory that uses a mathematical algorithm to quickly look up forwarding information. The forwarding information in the TCAM comes from the routing processes and traffic policies residing in the control plane of the switch.






0 comments:
Post a Comment